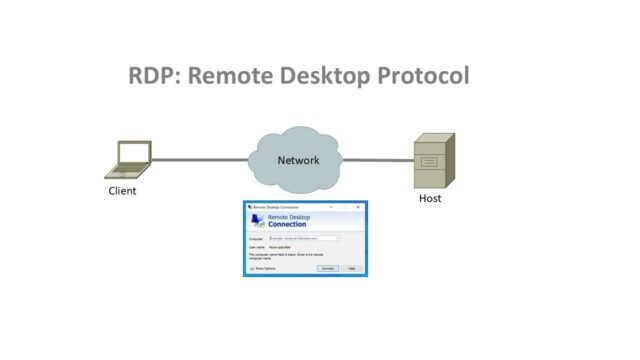
What is RDP?
RDP or Remote Desktop Protocol, is communication protocol developed by Microsoft, this protocol allows to control another computer remotely over a network connection.
With RDP, you can connect from client device to host (e.g. windows server or other PC/Laptop), your keyboard, mouse and display input/output are sent over the network. You can see the remote host’s desktop as if you were sitting in front of it, you can run applications there.
Very useful for administrators, remote support teams, however over the time, this was one of the most popular protocols used by hackers to compromise the system. RDP has inbuild vulnerabilities, which can be compromised very easily. On internet this is always be disabled. In 2019, more than 1 million devices were impacted due to BlueKeep vulnerability.
What are Secure Alternatives to RDP?
Secure Alternatives to RDP
Features
- No open ports on the internet
- Application level access only (not full network access)
- Always-on identity verification with MFA & device posture checks.
Examples
- Zscaler Private Access (ZPA)
- Palo Alto Prisma Access
- Cloudflare Access
- Netskope Private Access
Best for organizations wanted to replace RDP and traditional VPN entirely.
2. Bastion Hosts / Jump Servers
Features
- Users connect to a hardened, monitored intermediate server instead of directly to target machines.
- Session logging for auditing.
- No inbound RDP port exposure to the internet.
Examples
- Azure Bastion
- AWS Session Manager
- Teleport
Best for Admin access to sensitive servers.
3. Application Virtualization / Published Apps
Features
- Users only access the specific application they need, not an entire desktop.
- Reduces risk of lateral movement inside the network.
Examples
- Microsoft RemoteApp
- Citrix Virtual Apps
- VMware App Volumes
Best for organizations where workflows needing secure, app-only access.
4. Secure Remote Support Platforms
Features
- Encrypted connections via vendor’s relay servers.
- MFA, role-based permissions, and session recording.
- No need for direct inbound connectivity to corporate network.
Examples
- BeyondTrust Remote Support
- Splashtop Enterprise
- TeamViewer Tensor
Best for IT helpdesk, vendor/partner access.
5. SSH with MFA & Certificates (for Linux/CLI work)
Features
- Strong encryption, no default RDP exposure.
- Can enforce short-lived credentials & just-in-time access.
Examples
- OpenSSH + Duo MFA
- Teleport
- StrongDM
Best for DevOps, infrastructure teams.
6. Browser-based Remote Access
Features
- Access delivered through an HTTPS browser session.
- Sandboxed from local OS.
- Easy to restrict and monitor.
Examples
- Chrome Remote Desktop
- Citrix Secure Browser
- AWS WorkSpaces Web
Best for Contractors, temporary remote workers.
Security Comparison Table
| Method | Exposed Ports? | MFA Support | Session Logging | App-level Control | Complexity |
| ZTNA | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Medium |
| Bastion Host | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | Medium |
| Application Virtualization | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | High |
| Secure Remote Support Platforms | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Low-Medium |
| SSH + MFA/Certs | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | Medium |
| Browser-based Remote Access | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Low |
In high-security sectors like banking or pharma, the most common RDP replacement is ZTNA + Application Virtualization — this way, employees only get access to the specific apps they need, without the risks of an exposed RDP session.
